GPU Clusters on Civo Kubernetes
Overview
Running GPU workloads on Kubernetes is becoming increasingly common due to the flexibility and scalability it provides. Deciding on the type of Kubernetes nodes for your GPU workloads involves many considerations. Whether you require low-latency responses, high-throughput inference requests, or other performance needs, Civo has you covered.
GPU Types
Civo provides the following GPU Types:
- NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPU: Available in both 40GB and 80GB variants, this GPU is designed for high-demand workloads such as machine learning model training, large language models, and scientific computing. It offers significant computational power with over 312 teraflops of FP16 performance and 1,248 Tensor cores.
- NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU: Known for its advanced Hopper architecture, this GPU excels in AI training and inference tasks, making it ideal for developing and deploying large AI models like chatbots and recommendation engines.
- NVIDIA L40S GPU: With 48GB of GDDR6 memory, this GPU is suitable for tasks requiring a blend of AI computations and advanced graphics processing, such as 3D graphics rendering and training large language models.
- NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip: This GPU features an integrated CPU-GPU architecture tailored for generative AI, large-scale AI inference, and high-performance computing workloads that demand substantial memory and processing power.
To deploy GPU workloads on Kubernetes, add a new node pool to your cluster and refer to the details below to install the Kubernetes operator for GPU nodes.
GPU nodes for Kubernetes is a separate node SKU than traditional Kubernetes nodes.
Installing the NVIDIA GPU Operator on Civo Kubernetes
To take advantage of the Nvidia GPU in Civo Kubernetes clusters, you may wish to install a GPU operator to the cluster. This document details the following:
- Preparation of a Kubernetes cluster with a GPU node
- Installation of the GPU operator using Helm
- Troubleshooting
Preparation
Start by creating a Kubernetes cluster and allocate a GPU node to it following the instructions here.
You will also need to download the KUBECONFIG for the cluster once it is running.
In order to install the GPU operator, you will need to have Helm installed on the machine you are working on.
Now you should be able to use Kubectl to manage the Kubernetes Cluster.
Installation of the GPU operator using Helm
Once your KUBECONFIG is downloaded and set as your current context, you can run the following to deploy the GPU operator:
kubectl create ns gpu-operator
kubectl label --overwrite ns gpu-operator pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=privileged
helm repo add nvidia https://helm.ngc.nvidia.com/nvidia && helm repo update
helm install --wait --generate-name \
-n gpu-operator --create-namespace \
nvidia/gpu-operator
No upgrade the GPU operator to newer versions are needed - this process is fully automated.
Once you have deployed the GPU operator, run kubectl -n gpu-operator get pods to verify that the GPU operator is running well:
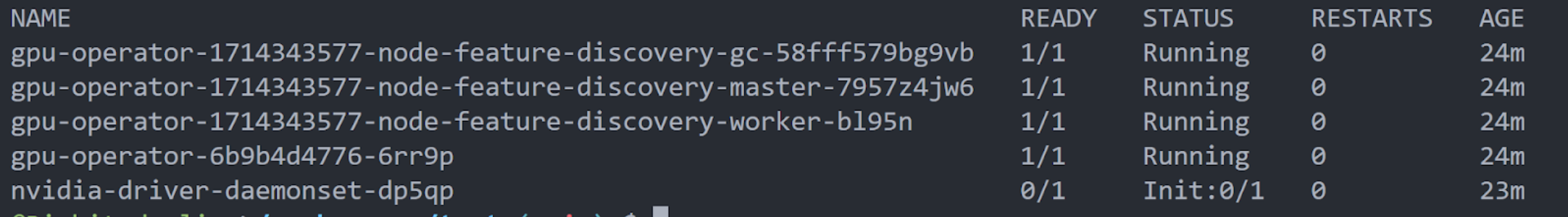
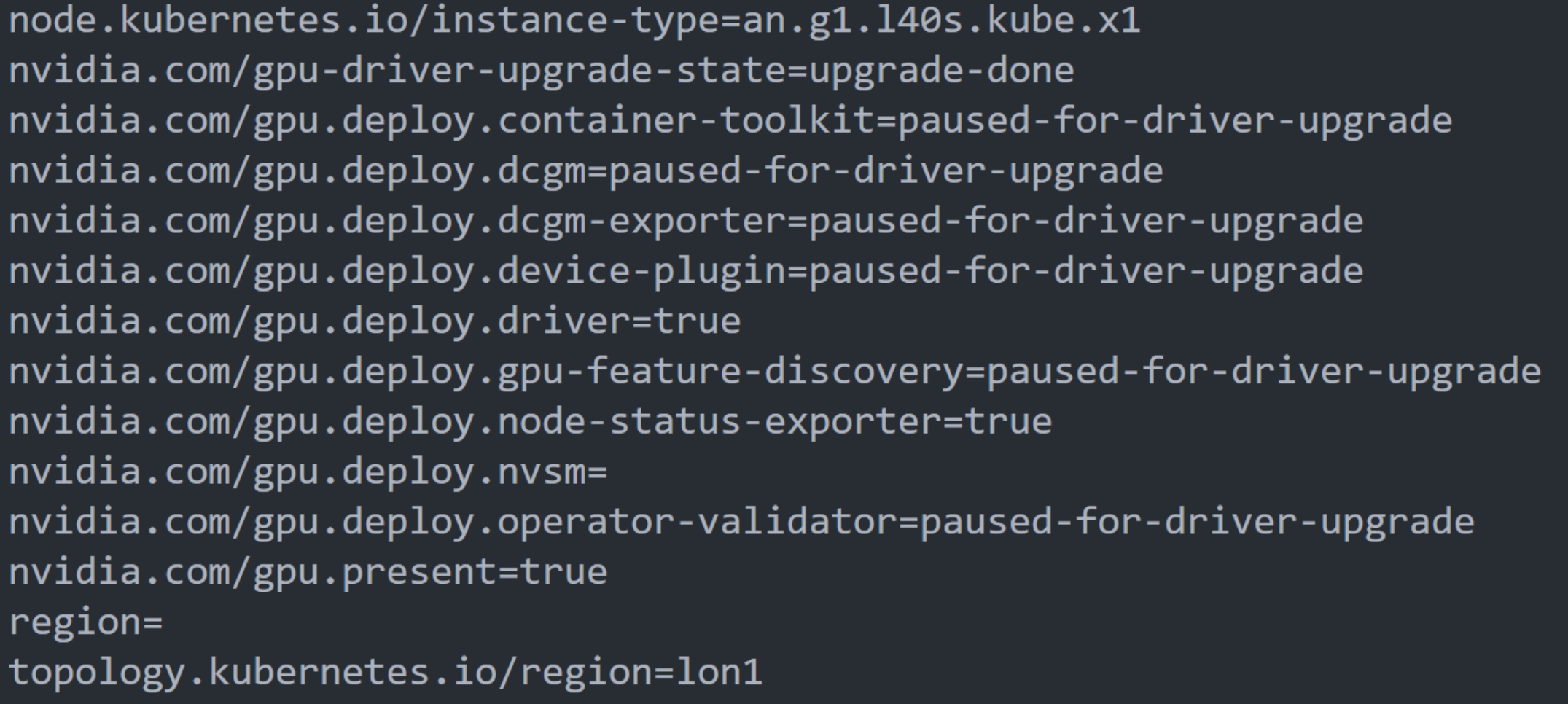
Now you are all set to use the GPU Operator, feel free to run kubectl describe nodes to verify that the GPU node was indeed classified to have a GPU, you would particularly see the following in the node’s labels:
Troubleshooting
If you experience any issues during the deployment (for example if you experience a timeout), you can reattempt the deployment by running the upgrade command:
export HELM_RELEASE_NAME=$(helm list --all-namespaces | awk 'NR>1 {print $1}') && helm upgrade $HELM_RELEASE_NAME nvidia/gpu-operator -n gpu-operator