Load Balancers
Overview
Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances, improving the performance and availability of your applications. You can create and configure load balancers through the Civo dashboard to route traffic to your instances with various distribution algorithms and health checking options.
Load balancers are billed hourly according to the current pricing. Additional costs apply for each subsequent 10,000 concurrent requests you configure the load balancer to handle. Usage is tracked as part of your billing and quota.
Creating a Load Balancer
You can create a load balancer from the Civo dashboard to distribute traffic across your instances.
Step 1: Navigate to Load Balancers
- Log in to your Civo dashboard.
- Navigate to Networking > Load Balancers in the left sidebar.
- Click Create Load Balancer.
Step 2: Configure Basic Settings
- Name: Enter a descriptive name for your load balancer.
- Network: Select which network the load balancer should use (see Network below).
- Firewall: Choose a firewall to control access (see Firewall below).
- Algorithm: Choose how traffic is distributed (see Algorithm below).
Step 3: Configure Instance Pool
- Targeting method: Choose to target instances by Tags or Names.
- Source port: The port on the load balancer that receives incoming traffic.
- Target port: The port on your instances where traffic is forwarded.
- Protocol: Select the protocol (HTTP, TCP, etc.).
- Health check port: The port to monitor for instance health.
- Health check path: The path to check for HTTP health checks (e.g.,
/healthz).
See Instance Pools for detailed configuration options.
Step 4: Set Capacity (Optional)
By default, load balancers handle 10,000 concurrent requests. Increase this limit if needed in Advanced options section.
Step 5: Create
Click Create Load Balancer to provision your load balancer. The load balancer will be assigned a public IP address once ready.
Instance Pools
Instance pools allow you to target specific groups of instances for traffic distribution. When configuring instance pools in the dashboard, you can specify:
Targeting Instances
You can target instances using either:
- Tags: Select instances that have specific tags assigned to them
- Names: Directly specify instance names to include in the pool
Note: Only use one method (tags or names) per instance pool, not both.
Port Configuration
For each instance pool, configure:
- Source Port: The port on the load balancer that will receive incoming traffic
- Target Port: The port on your instances where traffic should be forwarded
- Protocol: The protocol to use (HTTP, TCP, etc.)
Health Checks
Configure health check settings to ensure traffic is only sent to healthy instances:
- Health Check Port: The port on your instances to monitor for health status
- Health Check Path: The path to check for HTTP health checks (e.g.,
/healthz)
For detailed health check configuration including intervals, timeouts, and troubleshooting, see Load Balancer Health Checks.
Load Balancer Configuration Options
The following configuration options are available when creating a load balancer from the dashboard:
Algorithm
The load balancing algorithm determines how traffic is distributed across your instances:
- Round Robin (default): Requests are distributed evenly across all available instances in sequence
- Least Connections: Requests are sent to the instance with the fewest active connections
Network
You can select which network the load balancer should use to communicate with your instances. Choose from available networks in your account.
Firewall
Select which firewall rules to apply to your load balancer. You can choose from existing firewalls in your account or create a new one. If no firewall is specified, the load balancer will use the default firewall configuration.
To create a load balancer that is only accessible within your private network, see Internal Load Balancers.
Maximum Concurrent Requests
By default, load balancers are configured to handle 10,000 concurrent requests. You can increase this limit by entering a value above 10,000 in the dashboard. An additional charge is levied for each 10,000 requests above the default limit.
Updating the maximum concurrent requests will cause a brief period of downtime as the load balancer rebuilds.
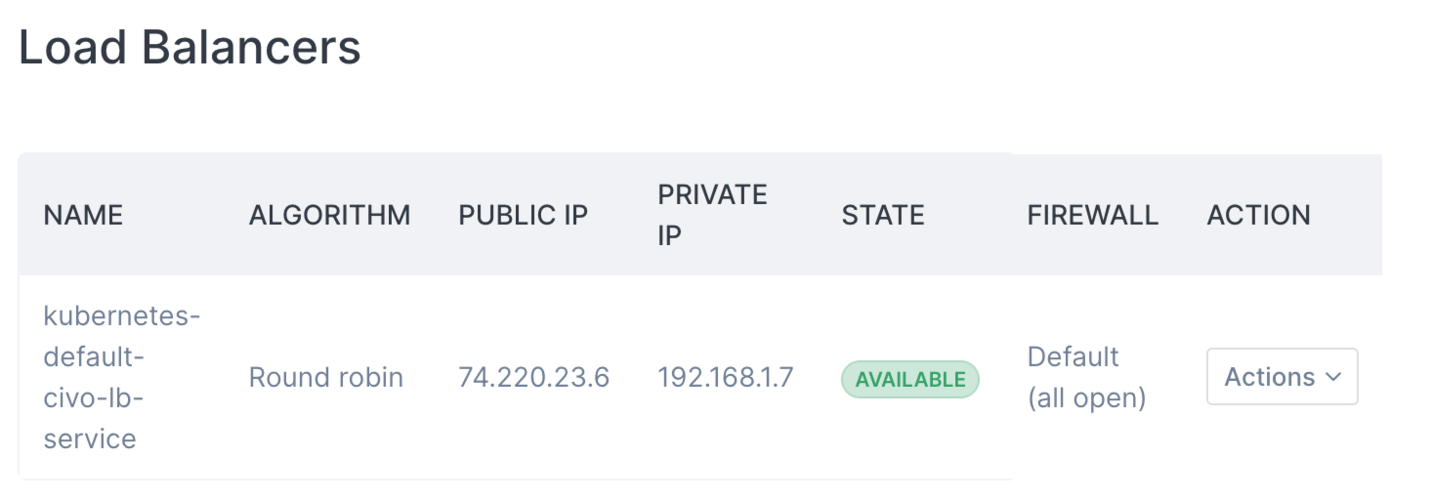
Viewing Load Balancer Details
You can view the current configuration of any load balancers on the load balancers listing page. From there, you can see details such as:
- Load balancer name and status
- Algorithm being used
- Public IP address
- Connected backends/instances
You can view more specific details of a particular load balancer by clicking on it or using the "Actions" menu and selecting "View".
Kubernetes Integration
When you create a Kubernetes Service of type LoadBalancer on a Civo Kubernetes cluster, a Civo load balancer is automatically provisioned and managed for you.
Automatic Load Balancer Creation
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
When this Service is applied, Civo automatically:
- Creates a load balancer
- Configures it to route traffic to your pods
- Assigns a public IP address (shown in
kubectl get svc)
Common Annotations
You can customize Kubernetes-managed load balancers using annotations:
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
kubernetes.civo.com/firewall-id | Attach a specific firewall by name or ID |
kubernetes.civo.com/loadbalancer-algorithm | Set the algorithm (round-robin or least-connections) |
civo.com/reserved-ip | Use a reserved IP address |
Example with annotations:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-app
annotations:
kubernetes.civo.com/firewall-id: "my-firewall"
kubernetes.civo.com/loadbalancer-algorithm: "least-connections"
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
When to Use Dashboard vs Kubernetes
| Use Dashboard | Use Kubernetes Service |
|---|---|
| Load balancing for standalone instances | Load balancing for Kubernetes workloads |
| Manual control over configuration | GitOps or declarative infrastructure |
| One-off or test deployments | Production Kubernetes deployments |
For Kubernetes workloads, let Kubernetes manage your load balancers. This ensures the load balancer stays in sync with your pods and is automatically cleaned up when the Service is deleted.
For internal-only load balancers in Kubernetes, see Internal Load Balancers.
Related Documentation
- Deleting a Load Balancer - Remove load balancers from your account
- Internal Load Balancers - Create load balancers accessible only within your private network
- Load Balancer Health Checks - Configure and troubleshoot health checks
- Firewalls - Control access to your load balancers
- Reserved IPs - Use static IP addresses with your load balancers